Nodes and Fields
Load a node and get a formatted text field
$nodeStorage = $this->entityTypeManager->getStorage('node');
$node = $nodeStorage->load(10706);
$body = $node->get('body')->value;
$body = $node->body->value;
//after text filters have done their magic!
$body = $node->body->processed;Retrieve a numeric field value
When you load a numeric field, Drupal returns a number i.e., 0, even if that field was never initialized with a value.
$accepted_votes = $feedback_error_node->get('field_accepted_votes')->value;
// Returns 0 if no value was entered into the field.Retrieve a text field value of comma-separated values into an array
If you have a text field with comma-separated values such as apple, pear, banana, you can retrieve them into an array directly like this:
$values_array = explode(',', $node->field_position_keywords->value);Retrieve a list field value
With a list field called field_tks_audience with the following values:
student|Student/Teacher
teacher|Teacher OnlyWhen you retrieve the field value, you get the key (or machine name), not the human-readable value. So if the field value is student then the following code will return student.
$audience = $node->get('field_tks_audience')->value;
// Or.
$audience = $citation_node->field_tks_audience->value;
// Or.
$audience = $node->get('field_tks_audience')->getString();If you want the human-readable value, you can use the combination of `getFieldDefinition()->getSetting('allowed_values') which returns an array of possible results indexed by the key:
$audience_key = $citation_node->field_tks_audience->value;
$audience_values = $citation_node->field_tks_audience->getFieldDefinition()->getSetting('allowed_values');
$audience_human_readble_string = $audience_values[$audience_key];
Note
You can produce safe HTML using the FieldFilteredMarkup class. This may be a good way to display user-entered HTML without risking XSS attacks. Be aware that this class is marked as @internal because it should only be used by the Field module and field-related plugins. Of course, this is not necessary for a list field, but it is useful for text fields.
// This filters the string using a very restrictive tag list when it is created.
$audience_value = FieldFilteredMarkup::create($audience_values[$audience_key]);Set field values
$node->set('field_tks_subchapter', $subchapterFullStatement);
$node->set('field_tks_standard_type', "TEKS");
$node->save();Get current page title
Use this in a controller to return the current page title.
$request = \Drupal::request();
if ($route = $request->attributes->get(\Symfony\Cmf\Component\Routing\RouteObjectInterface::ROUTE_OBJECT)) {
$title = \Drupal::service('title_resolver')->getTitle($request, $route);}Test if variable is a node
// Is this variable a node?
if ($ref instanceof EntityInterface && $ref->getEntityTypeId === 'node') {
// yep
}Get the current nid, node type and title
Here are two ways to retrieve the current node -- via the request or using the route
$node = \Drupal::request()->attributes->get('node');
$nid = $node->id();OR
$node = \Drupal::routeMatch()->getParameter('node');
if ($node instanceof \Drupal\node\NodeInterface) {
// You can get nid and anything else you need from the node object.
$nid = $node->id();
$nodeType = $node->bundle();
$nodeTitle = $node->getTitle();
}If you need to use the node object in hook_preprocess_page() on the preview page, you need to use the node_preview parameter, instead of the node parameter:
function mymodule_preprocess_page(&$vars) {
$route_name = \Drupal::routeMatch()->getRouteName();
if ($route_name == 'entity.node.canonical') {
$node = \Drupal::routeMatch()->getParameter('node');
}
elseif ($route_name == 'entity.node.preview') {
$node = \Drupal::routeMatch()->getParameter('node_preview');
}And from https://drupal.stackexchange.com/questions/145823/how-do-i-get-the-current-node-id when you are using or creating a custom block, then you have to follow this code to get the current node id. Not sure if it is correct
use Drupal\Core\Cache\Cache;
$node = \Drupal::routeMatch()->getParameter('node');
if ($node instanceof \Drupal\node\NodeInterface) {
$nid = $node->id();
}
// for cache
public function getCacheTags() {
//With this when your node changes your block will rebuild
if ($node = \Drupal::routeMatch()->getParameter('node')) {
//if there is node add its cachetag
return Cache::mergeTags(parent::getCacheTags(), ['node:' . $node->id()]);
}
else {
//Return default tags instead.
return parent::getCacheTags();
}
}
public function getCacheContexts() {
//if you depend on \Drupal::routeMatch()
//you must set context of this block with 'route' context tag.
//Every new route this block will rebuild
return Cache::mergeContexts(parent::getCacheContexts(), ['route']);
}Retrieve current node id (nid)
If the site is currently displaying node/123, this will return a path node/123.
$current_path = \Drupal::service('path.current')->getPath();Also
$node = \Drupal::routeMatch()->getParameter('node');
if ($node instanceof \Drupal\node\NodeInterface) {
// You can get nid and anything else you need from the node object.
$nid = $node->id();
$nodeTitle = $node->getTitle();
$nodeType = $node->bundle();
if ($nodeType != 'unit') {
return;
}Retrieve node info from current path
You don't need to load the node
$node = \Drupal::routeMatch()->getParameter('node');
if ($node instanceof \Drupal\node\NodeInterface) {
// You can get nid and anything else you need from the node object.
$nid = $node->id();
if ($node->getType() == 'unit') {
$contract_id = $node->field_contract_id->value;
$facebook = $node->field_facebook->value;
}
}Load the current node and get its node id (nid), field, type
To grab some information from the currently displayed node, use the \Drupal object::routeMatch().
// Grab current node.
$node = \Drupal::routeMatch()->getParameter('node');
if ($node instanceof \Drupal\node\NodeInterface) {
// You can get nid and anything else you need from the node object.
$nid = $node->id();
if ($node->getType() == 'unit') {
$v = $node->get('field_footer_social_media_headin')->value;
if (!empty($v)) {
...
}
$v = $node->get('field_facebook')->value;
if (!empty($v)) {
...
}Note, you can also $node->get('field_facebook')->getValue() which returns an array of values. This is a good way to retrieve unlimited value fields i.e. fields that have more than 1 value.
Load a node by nid and get its title, type and a field
From: https://www.drupal.org/docs/8/api/entity-api/working-with-the-entity-api
use Drupal\node\Entity\Node;
// Using the node id = 1.
$node = Node::load(1);Or
$node = \Drupal::entityTypeManager()->getStorage('node')->load(1);
$headline = $node->getTitle();
// What type of node is that?
$type = $node->getType();
// Get the URL field.
$url = $node->get('field_url')->value;Or
$node_storage = \Drupal::entityTypeManager()->getStorage('node');
$node = $node_storage->load(1);
$url = $node->get('field_url')->value;Or
$body = $node->field_srp_pc_change_type->value;And multivalue fields are similar. They are loaded when you use get & getValue or the magic getter & getValue. You can then loop through the returned values:
$topics = $node->get('field_news_topics_for_listing')->getValue(); //get.or
$topics = $node->field_news_topics_for_listing->getValue(); //magic getter.
foreach ($topics as $topic) {
// Do something.
}Load the current node and get the nid, field, type
// For content type unit grab their facebook/instagram, etc.
$node = \Drupal::routeMatch()->getParameter('node');
if ($node instanceof \Drupal\node\NodeInterface) {
// You can get nid and anything else you need from the node object.
$nid = $node->id();
if ($node->getType() == 'unit') {
$sm_heading = $node->get('field_footer_social_media_headin')->value;
if (!empty($sm_heading)) {
...
}
$fb = $node->get('field_facebook')->value;
if (!empty($fb)) {
...
}Note, you can also
$node->get('field_facebook')->getValue();Which returns an array of values.
Load the user id (uid) for a node
$my_node->getOwnerId();You can call $node->uid but that returns an EntityReferenceFieldItemList with all sorts of juicy information. The user id is in there, but it's more challenging to extract.
Test if a field is empty
$entity->get('field_name')->isEmpty()To avoid the warning message Attempt to read property "target_id" on null you can use the following:
For an entity reference field use:
$sf_contract_node = Node::load($sf_contract_nid);
if (!$sf_contract_node->get('field_vendor_url')->isEmpty()) {
$url = $sf_contract_node->field_vendor_url->first()->getUrl();
$url = $url->getUri();
$variables['vendor_url'] = $url;
}And more concisely:
$url = $sf_contract_node?->field_vendor_url?->first()?->getUrl();
if (!is_null($url)) {
$uri = $url->getUri();
}For a single value entity reference field:
$nid = 0;
if (!isset($node->get('field_my_entity_ref_field')->target_id)) {
$nid = $node->get('field_my_entity_ref_field')->target_id;
}Test if a multivalue entity reference field is empty
To avoid the warning message Attempt to read property "target_id" on null you can use the following:
// If there is a value at the specified index, then return the target_id, otherwise, return 0.
$team_nid = 0;
if (isset($program_node->get('field_srp_team_ref')[$vote_number]->target_id)) {
$team_nid = $program_node->get('field_srp_team_ref')[$vote_number]->target_id;
}And more concisely:
// If there is a value at the specified index, then return the target_id, otherwise, return 0.
$vote_number = 3;
// These are zero-based.
$team_nid = $program_node->get('field_srp_team_ref')[$vote_number]->target_id ?? 0;Load a node and update a field
$node = \Drupal::entityTypeManager()->getStorage('node')->load(1);
$url = $node->set('field_url', 'the-blahblah');
$node->save();Retrieve values from a date range field
Start date and then end date
$node->get('field_cn_start_end_dates')->value
$node->get('field_cn_start_end_dates')->end_valueRetrieve a multivalue field
Multivalue fields can be loaded with get('fieldname') or using a magic field getter like $node->field_my_field. Adding ->getValue() to the end of either of these calls returns a simple array.
For example, a multivalue text field will return an array of values like this:
$data = $node->get('field_condiment')->getValue();
// returns:
$data[0]['value'] = 'ketchup'
$data[1]['value'] = 'mayo'
$data[2]['value'] = 'reference'However, a multivalue entity reference field (including taxonomy) will return values with the target_id array key. e.g.
$data = $node->get('field_event_ref')->getValue();
// returns:
$data[0]['target_id'] = 1
$data[1]['target_id'] = 2
$data[2]['target_id'] = 14Iterate through results
Using $node->field_condiment or $node->get('field_condiment') returns a Drupal\Core\Field\FieldItemList which is iteratable. You can loop through the results and retrieve the values like this:
$items = $node->field_condiment;
foreach ($items as $item) {
$result = $item->value;
// For entity reference fields use
// $result_nid = $item->target_id;
}For entity reference fields, use ->target_id rather than ->value.
And you can check if there is a particular item in the array like this:
// get FieldItemList.
$condiments = $node->get('field_condiment');
$vote_number = 1;
if (isset($condiments[$vote_number])) {
$result = $condiments[$vote_number]->value;
}
// $result is ketchup.
// Or the PHP 8 way:
$result= $node->field_condiment?->get($vote_number)?->value;
// OR
$result = $node->field_condiment[$vote_number]?->value;Read a specific instance
You can directly reference an item by specifying an array offset. The index key (0 or 1 below) can also be referred to as the delta.
$status = $node->get('field_voting_status')[0]->value;
$status = $node->get('field_voting_status')[1]->value;Note, if the value for delta 1 is empty, Drupal will throw a warning message *Warning*: Attempt to read property "value" on null in ...
So rather than reading the [1]->value directly, you should check if there is a value using isset() and then you can read the ->value. Note, when you do the isset() test, you don't add the ->value at the end e.g.
if(!is_null($node->get('field_voting_status')[$vote_number])) {
$voting_status = $correlation_node->field_voting_status[$vote_number]->value;
}Utility function to read multivalue fields
/**
* Returns array of data for multivalue node reference fields.
*
* @param \Drupal\Core\Field\FieldItemListInterface $ref_field
* The entity reference field which we are building the links from.
* @param string $param_name
* Parameter name to be passed as get value.
* @param string $value_type
* Indicates which field to retrieve from database.
* @param string $field_ref_type
* Variable to determine type of reference field.
*
* @return array
* Array of data.
*
* @throws \Drupal\Component\Plugin\Exception\InvalidPluginDefinitionException
* @throws \Drupal\Component\Plugin\Exception\PluginNotFoundException
*/
function getMultivalueReferenceData(FieldItemListInterface $ref_field, string $param_name, string $value_type, string $field_ref_type = 'node') {
$values = [];
$title = '';
if ($ref_field) {
foreach ($ref_field as $ref) {
if ($field_ref_type == 'taxonomy') {
$term = Drupal::entityTypeManager()
->getStorage('taxonomy_term')
->load($ref->$value_type);
if ($term) {
$title = $term->getName();
}
}
else {
if ($value_type == 'value') {
$title = $ref->$value_type;
}
else {
if (isset($ref->entity->title->value)) {
$title = $ref->entity->title->value;
}
}
}
$id = $ref->$value_type;
$values[] = [
'title' => $title,
'id' => str_replace(' ', '+', $id),
'param_name' => $param_name,
];
}
}
return $values;
}Update a multivalue field
This can be a little tricky, especially if you want to preserve the existing values in the field.
Here, I used the getValue() to load all the values. This returns an array of values like:
$data = $node->get('field_event_ref')->getValue();
$result0 = $data[0]['value'];
$result1 = $data[1]['value'];So to update one of them, I want to do something like this: $data[1]['value']='flour';.
e.g. I load up the current values, fill in the 6th [5] item, and save them. This preserves the existing values in positions [0] through [4].
$values = $node->get('field_voting_status')->getValue();
$values[5]['value'] = 'incomplete';
$node->set('field_srp_voting_status', $values);
$node->save();Function to read and write multivalue fields
Here is a function which reads and writes multivalue fields safely. You pass it the $node->field_name, the index (vote_number), etc., and then it builds and returns an array formatted for updating the field data. It can also update the array if you pass in a value.
It could probably be genericized further.
public static function getMultivalueFieldArrayOfValues($values_field_data, $vote_number = 0, $new_value = NULL, $field_type = 'value', $default_value = NULL) {
$values_array = [];
foreach($values_field_data as $data) {
$values_array[] = [
$field_type => $data->value,
];
}
if(!is_null($new_value)) {
//CHECK FOR PREVIOUS VALUES. IF THEY DO NOT EXIST SET TO NEW VALUE
for($i=0; $i<=$vote_number; $i++) {
if(!isset($values_array[$i])) {
if(!is_null($default_value)) {
$values_array[$i] = $default_value;
}
else {
$values_array[$i] = $new_value;
}
}
}
if(isset($values_array[$vote_number])) {
$values_array[$vote_number] = [$field_type => $new_value];
}
else {
$values_array[] = [$field_type => $new_value];
}
}
return $values_array;
}Example of using the above function for reading data and then writing the data without using it:
// Retrieve current field values for correlation narrative/activity status fields
$activity_status = 'accepted';
$activity_statuses = $node->field_activity_status;
$activity_status_values = self::getMultivalueFieldArrayOfValues($activity_statuses);
$activity_status_values[0]['value'] = $activity_status;
$narrative_status = 'accepted';
$narrative_statuses = $node->field_narrative_status;
$narrative_status_values = self::getMultivalueFieldArrayOfValues($narrative_statuses);
$narrative_status_values[0]['value'] = $narrative_status;
$node->set('field_narrative_status', $narrative_status_values);
$node->set('field_activity_status', $activity_status_values);
$node->save();Save multivalue field, entity reference field
When you really care which delta/index/offset, you can specify that offset. It's a bit confusing how exactly it works. For text or numeric fields, it works like you'd expect. You can just specify the offset. For entity reference fields, you have to do some fiddling. Don't use $node->set() as this overwrites everything in the field, rather use the magic field setter variable and specify the offset.
Here, $vote_number represents the index, so if $vote_number = 0, this writes the first item in the multivalue field. If $vote_number = 1, then write the second item, and so on.
$citation_node->field_srp_voting_status[$vote_number] = 'incomplete';Be cautious, you might think this would work, but it doesn't
$program_node->set('field_srp_team_ref', [$vote_number => 1234]);If you are going to write index 2 and there is a possibility that there isn't an index 0 and 1, you need something like this (in protected function correlationSanityCheckFix(Node $correlation_node)):
$narrative_status = '';
if (!is_null($correlation_node->get('field_narrative_status')[$vote_number])) {
$narrative_status = $correlation_node->get('field_narrative_status')[$vote_number]->value;
}
if (empty($narrative_status)) {
// Grab all the statuses and add mine.
$statuses = $correlation_node->get('field_narrative_status');
$new_statuses = [];
foreach ($statuses as $status) {
$new_statuses[] = $status->value;
}
$new_statuses[$vote_number] = 'incomplete';
$correlation_node->set('field_narrative_status', $new_statuses);
$save_correlation = TRUE;
}Update a multivalue entity reference fields
When writing multivalue entity reference fields, you have to load up the previous values, build an array of target_ids (node ids) and then write them all in one pass with a $node->set() method.
$teams = $new_program_node->get('field_srp_team_ref');
$new_teams = [];
foreach ($teams as $team) {
$new_teams[] = $team->target_id;
}
$new_teams[$new_program_vote_number] = $team_id;
$new_program_node->set('field_srp_team_ref', $new_teams);Generic Multivalue field writer
Here is a generic function that knows how to write values in a "sane" way.
/**
* Smart multivalue field setter.
*
* Example calls:
*
* Set the index 2 to incomplete, keep old values:
* smartMultiValueFieldSetter($node, 'field_srp_voting_status', 'incomplete', 2);
*
* Set the index 1 to incomplete, overwrite the old values to 'placeholder'
* smartMultiValueFieldSetter($node, 'field_srp_voting_status', 'incomplete', 1, 'placeholder', TRUE);
*
*
* @param \Drupal\node\Entity\Node $node
* Node.
* @param string $field_name
* Field name.
* @param string $value
* Value to be put in $node->field[$index]->value.
* @param int $index
* The delta i.e. $node->field[$index]
* @param string $default_value
* The default values that will be written into the previous indexes.
* @param bool $overwrite_old_values
* TRUE to ignore previous index values and overwrite them with $default_value.
*/
public static function smartMultiValueFieldSetter(Node $node, string $field_name, string $value, int $index, string $default_value="", bool $overwrite_old_values=FALSE) {
$old_values = $node->get($field_name)->getValue();
// Grab old values and put them into $new_values array.
$field_type = $node->get($field_name)->getFieldDefinition()->getType();
if ($field_type == 'entity_reference') {
foreach ($old_values as $key=>$old_value) {
$new_values[$key] = $old_values[$key];
}
}
else {
$new_values = [];
foreach ($old_values as $old_value) {
$new_values[]["value"] = $old_value["value"];
}
}
// Ignore what was in the old values and put my new default value in.
if ($overwrite_old_values) {
for ($i = 0; $i < $index; $i++) {
$new_values[$i] = $default_value;
}
}
// Pad missing items.
for ($i = 0;$i<$index; $i++) {
if (!isset($new_values[$i])) {
if ($field_type == 'entity_reference') {
$new_values[$i] = $default_value;
}
else {
$new_values[$i]['value'] = $default_value;
}
}
}
if ($field_type == 'entity_reference') {
$new_values[$index]['target_id'] = $value;
}
else {
$new_values[$index]["value"] = $value;
}
// Trim off extras from testing.
// TODO: this isn't trimming correctly for entity ref fields.
if (count($new_values)>($index+1)) {
$chunk = array_chunk($new_values, $index+1);
$new_values = $chunk[0];
}
$node->set($field_name, $new_values);
}Here is an example of using the above function to write values to the field_condiment which is a multivalue text field.
$node = Node::load(35);
// Write to index 0, 1, 2.
self::smartMultiValueFieldSetter($node, 'field_condiment', 'ketchup', 0);
self::smartMultiValueFieldSetter($node, 'field_condiment', 'mayo', 1);
self::smartMultiValueFieldSetter($node, 'field_condiment', 'mustard', 2);
$node->save();
// Write into index position 2 and pad the previous values with "dummy".
self::smartMultiValueFieldSetter($node, 'field_condiment', 'mustard', 2, 'dummy', TRUE);
$node->save();
// Write into index position 1 and pad position 0 with "dummy", and remove the contents of index 2.
self::smartMultiValueFieldSetter($node, 'field_condiment', 'ketchup', 1, 'dummy', TRUE);
$node->save();Here is a complete function from the controller GeneralController.php. There are a wide variety of calls to smartMultiValueFieldSetter() showing its use with multivalue text and entity-reference fields (including a taxonomy field):
public function multiTest() {
$str = '<h2>Results</h2>';
$node = Node::load(35);
// Write to index 0, 1, 2.
self::smartMultiValueFieldSetter($node, 'field_condiment', 'ketchup', 0);
self::smartMultiValueFieldSetter($node, 'field_condiment', 'mayo', 1);
self::smartMultiValueFieldSetter($node, 'field_condiment', 'mustard', 2);
//$node->save();
$field_name = 'field_condiment';
$field_type = $node->get($field_name)->getFieldDefinition()->getType();
$contents = $node->get($field_name)->getValue();
$str .= "<br/><strong>Field:</strong> " . $field_name;
$str .= ", type: " . $field_type;
$str .= "<br/><strong>Values: </strong>";
foreach ($contents as $item) {
$str .= $item['value'] . ', ';
}
self::smartMultiValueFieldSetter($node, 'field_condiment', 'mustard', 2, 'dummy', TRUE);
$contents = $node->get($field_name)->getValue();
$str .= "<br/><strong>Values: </strong>";
foreach ($contents as $item) {
$str .= $item['value'] . ', ';
}
self::smartMultiValueFieldSetter($node, 'field_condiment', 'ketchup', 1, 'dummy', TRUE);
$contents = $node->get($field_name)->getValue();
$str .= "<br/><strong>Values: </strong>";
foreach ($contents as $item) {
$str .= $item['value'] . ', ';
}
$field_name = 'field_event';
$field_type = $node->get($field_name)->getFieldDefinition()->getType();
$contents = $node->get($field_name)->getValue();
//kint($contents);
$str .= "<br/><strong>Field:</strong> " . $field_name;
$str .= ", type: " . $field_type;
$str .= "<br/><strong>Values: </strong>";
foreach ($contents as $item) {
$str .= $item['target_id'] . ', ';
}
// 17, 18
//14, 18, 19
self::smartMultiValueFieldSetter($node, $field_name, 14, 0);
self::smartMultiValueFieldSetter($node, $field_name, 18, 1);
self::smartMultiValueFieldSetter($node, $field_name, 19, 2);
$contents = $node->get($field_name)->getValue();
$str .= "<br/><strong>Values: </strong>";
foreach ($contents as $item) {
$str .= $item['target_id'] . ', ';
}
$field_name = 'field_category';
$field_type = $node->get($field_name)->getFieldDefinition()->getType();
$contents = $node->get($field_name)->getValue();
//kint($contents);
$str .= "<br/><strong>Field:</strong> " . $field_name;
$str .= ", type: " . $field_type;
$str .= "<br/><strong>Values: </strong>";
foreach ($contents as $item) {
$str .= $item['target_id'] . ', ';
}
// 3, 2, 1
// 1, 2, 3.
self::smartMultiValueFieldSetter($node, $field_name, 1, 0);
self::smartMultiValueFieldSetter($node, $field_name, 2, 1);
self::smartMultiValueFieldSetter($node, $field_name, 3, 2);
$contents = $node->get($field_name)->getValue();
//kint($contents);
$str .= "<br/><strong>Values: </strong>";
foreach ($contents as $item) {
$str .= $item['target_id'] . ', ';
}
// Multivalue Text Field.
$field_name = 'field_condiment';
// Returns FieldItemList.
$data = $node->get($field_name);
$data = $node->field_condiment;
// Returns simple array.
$data = $node->get($field_name)->getValue();
$data = $node->field_condiment->getValue();
// Multivalue entity reference field.
$field_name = 'field_event';
$data = $node->get($field_name)->getValue();
$data = $node->field_event;
// Multivalue taxonomy entity reference field.
$field_name = 'field_category';
$data = $node->get($field_name)->getValue();
// Yes, you can use a variable for a magic field getter!
$data = $node->$field_name;
// Loop thru results.
$items = $node->field_condiment;
foreach ($items as $item) {
$x = $item->value;
}
// get array of results.
$condiments = $node->get('field_condiment');
$vote_number = 1;
if (isset($condiments[$vote_number])) {
$result = $condiments[$vote_number]->value;
}
$result = $node->get('field_condiment')[0]->value;
$result = $node->get('field_condiment')[5]->value;
if (isset($node->get('field_condiment')[2]->value)) {
$result = $node->get('field_condiment')[2]->value;
}
$render_array['content'] = [
'#type' => 'item',
'#markup' => $str,
];
return $render_array;
}Does this field exist in my entity?
To check if a field exists in a node.
$entity->hasField('abc');e.g. Here we load a field field_library_media from a node, grab its target id (which we happen to know is a media entity). We load the media entity and check if there is a field called field_media_document. This rather convoluted example is used to get the file size of the file in the media field.
use Drupal\media\Entity\Media;
use Drupal\file\Entity\File;
$media_id = $node->field_library_media->target_id;
if ($media_id) {
$media_item = Media::load($media_id);
// Get the file.
if ($media_item->hasField('field_media_document')) {
$file_id = $media_item->field_media_document->getValue()[0]['target_id'];
}
if (isset($file_id)) {
$file = File::load($file_id);
if ($file) {
// Get file size.
$file_size = format_size($file->getSize());
// Set file size variable.
$variables['file_size'] = $file_size;
}
}
}Get URL for an image or file in a media reference field
$node = Node::load($nid);
if ($node) {
$id = $node->field_banner_image->target_id;
$media = Media::load($id);
//Not always correct
//$fid = $media->field_media_image->target_id;
//Better way:
$fid = $media->getSource()->getSourceFieldValue($media);
$file = File::load($fid);
if ($file) {
$uri = $file->getFileUri();//URI e.g. public://2020-12/atom.jpg
$media_url = file_create_url($uri); //Full URL of uploaded image.
//E.g. https://dir.ddev.site/sites/default/files/2020-12/atom.jpg
}
\Drupal::messenger()->addMessage("field_banner image URL is $media_url");
$variables['program_area_banner_image_url'] = $media_url;
}You can get relative or absolute paths using one of these
$file = File::load($fid);
if ($file) {
$uri = $file->getFileUri(); //returns drupal filename e.g. public://2020-12/atom.jpg
$file_url = file_create_url($uri); //returns absolute file URL e.g. https://...file.jpg
//also
$absolute_file_url = $file->createFileUrl(FALSE); //returns absolute file path (url)
$relative_file_url = $file->createFileUrl(TRUE); //returns relative file path (url)Retrieve info about a file field
Here we have a file field called field_materials_file that we loaded from a paragraph. Looking in core/modules/file/src/Entity/File.php we can see a series of useful functions like getFileName(), getFileUri(),getSize(), getCreatedTime(). To use these, we have to append ->entity after the field, as shown below
$file = $para->field_materials_file;
$filename = $file->entity->getFileName();
$uri = $file->entity->getFileUri();Since File is an entity, we can also look in EntityBase.php to find more useful functions like id(), label(), bundle().
Retrieve values from a link field
Here we have a link field: field_link which we load and get a valid URI from it using:
$link = $para->field_link;
$link_uri = $para->field_link->uri;Or
$current_url = $correction->get('field_link')->uri;Or
In a .module file, first() returns a Drupal\link\Plugin\FieldType\LinkItem
if ($sf_contract) {
$vendor_url = $sf_contract->field_vendor_url->first();
if ($vendor_url) {
// this works too: $vendor_url = $vendor_url->uri;
$vendor_url = $vendor_url->getUrl(); // returns a Drupal\Core\Url.
$vendor_url = $vendor_url->toString();
_add_single_metatag("vendor_url", $vendor_url, $variables);
}Leaving off the ->first() (like this) returns a Drupal\Core\Field\FieldItemList which is a list of fields so you then would have to pull out the first field and extract the URI out of that.
$vendor_url = $sf_contract->field_vendor_url;Does this field exist in my entity?
$entity->hasField('abc');e.g. Here we load a field field_library_media from a node, grab its target id (which we happen to know is a media entity). We load the media entity and check if there is a field called field_media_document. This rather convoluted example is used to get the file size of the file in the media field.
$media_id = $node->field_library_media->target_id;
if ($media_id) {
$media_item = Media::load($media_id);
// Get the file.
if ($media_item->hasField('field_media_document')) {
$file_id = $media_item->field_media_document->getValue()[0]['target_id'];
}
if (isset($file_id)) {
$file = File::load($file_id);
if ($file) {
// Get file size.
$file_size = format_size($file->getSize());
// Set file size variable.
$variables['file_size'] = $file_size;
}
}
}Create a node and write it to the database
use \Drupal\node\Entity\Node;
// Create node object.
$node = Node::create([
'type' => 'article',
'title' => 'Druplicon test',
]);
$node->save();Create a node with an image
use \Drupal\node\Entity\Node;
use \Drupal\file\Entity\File;
// Create file object from remote URL.
$data = file_get_contents('https://www.drupal.org/files/druplicon.small_.png');
$file = file_save_data($data, 'public://druplicon.png', FILE_EXISTS_REPLACE);
// Create node object with attached file.
$node = Node::create([
'type' => 'article',
'title' => 'Druplicon test',
'field_image' => [
'target_id' => $file->id(),
'alt' => 'Hello world',
'title' => 'Goodbye world'
],
]);
$node->save();Write a node with an attached file
use \Drupal\node\Entity\Node;
use \Drupal\file\Entity\File;
// Create file object from remote URL.
$data = file_get_contents('https://www.drupal.org/files/druplicon.small_.png');
$file = file_save_data($data, 'public://druplicon.png', FILE_EXISTS_REPLACE);
// Create node object with attached file.
$node = Node::create([
'type' => 'article',
'title' => 'Druplicon test',
'field_image' => [
'target_id' => $file->id(),
'alt' => 'Hello world',
'title' => 'Goodbye world'
],
]);
$node->save();To populate the fields of an entity, you can either use the $entity->set($key, $value) method on the entity object or pass a key=>value array to the entity constructor. As such:
$foo = new Foo([
'name' => 'bar',
'baz' => TRUE,
'multi_value' => [
'first',
'second',
'third',
]
]);Write taxonomy field
$entity->set('field_file_type', 145);
// OR.
$entity->set('field_file_type', ['target_id' => 145]);Write a date or datetime to a node
note the [] array stuff is optional
//DateTime:
$dateTime = \DateTime::createFromFormat('Y-m-d','2000-01-30');
$newDateTimeString = $dateTime->format('Y-m-d\TH:i:s');
// Create node object
$node = Node::create([
'type' => 'workshop',
'title' => 'selwyn test' . (string) random_int(1,200),
'field_workshop_start_date' => ['2017-12-05',], //date only
'field_workshop_end_date' => [$newDateTimeString,], //DateTimeOr just a date (no time)
$dateTime = \DateTime::createFromFormat('Y-m-d','2000-01-30');
$newDateString = $dateTime->format('Y-m-d');
...
'field_workshop_other_date' => [$newDateString,],Set field values
$node->set('field_tks_subchapter', $subchapterFullStatement);
$node->set('field_tks_standard_type', "TEKS");
$node->save();And the shortened version (from https://gorannikolovski.com/blog/various-ways-updating-field-values-drupal-8-and-9 )
$node->field_tks_subchapter = $subchapterFullStatement;
$node->field_tks_standard_type = “TEKS";
$node->save();Also
$node->field_tks_subchapter->value = $subchapterFullStatement;
$node->field_tks_standard_type->value = “TEKS";
$node->save();Set an entity reference field
//That is the node id.
$node->field_name->target_id = 123;
// You can assign an entity object.
$entity->set('field_name', $another_entity);
$node->field_tks_standard_type->value = “TEKS";
$node->save();Set multivalue fields (regular and entity reference)
//The multivalue fields are no different. You just have to use arrays. So, instead of this:
$entity->field_name_muti->value = ['foo', 'bar', 'baz'];
$entity->field_name_multi->target_id = [1, 2, 3]
$entity->field_name_multi->target_id = [$another_entity1, $another_entity2, $another_entity3]
// You can use this:
$entity->field_name_muti = ['foo', 'bar', 'baz'];
$entity->field_name_multi = [1, 2, 3]
$entity->field_name_multi = [$another_entity1, $another_entity2, $another_entity3]Also, if you just want to update a specific one, specify the delta like this
$expectation_node->set('field_name_multi',[0 => 'foo']);
$expectation_node->set('field_name_multi',[1 => 'bar']);Or with variables...
$expectation_node->set('field_srp_teacher_voting_status',[$current_vote_number => $voting_status]);Clear a text field
Single text field
$node->set('field_subtitle', NULL);Set a formatted text/body field
To write to a long text field, be sure to specify the text format.
$text = 'this is some text to go in the body field';
$node->set('body', [
'summary' => $summary,
'value' => $text,
//'format' => 'full_html',
//'format' => 'basic_html',
//'format' => 'restricted_html',
//'format' => 'plain_text',
'format' => 'links_bullets_headings_and_images',
]);Alternatively.
$text = 'this is some text to go in the body field';
$node->field_info = [
'value' => $text,
'format' => 'links_and_bullets',
];Clear a formatted text/body field
To empty a body field, use this:
$node->body = [];
$node->body = NULL;Load a node and retrieve an entity reference node and nid (target_id)
$node_storage = \Drupal::entityTypeManager()->getStorage('node');
$node = $node_storage->load($nid);
//Same
$ref_nid = $node->get('field_sf_contract_ref')->target_id;
//or
$ref_nid = $node->field_sf_contract_ref->target_id;Load a multivalue reference field.
Here, node 35 has a field_event (multivalue entity reference field) with several values. This code shows how to retrieve the first one, get it's nid and its title:
$node = Node::load(35);
// Get an array of nodes.
$node_array = $node->get('field_event')->referencedEntities();
// Pop one off with reset.
$ref_node = reset($node_array);
$nid = $ref_node->id();
$title = $ref_node->getTitle();As $ref_node is a node object, you retrieve any field value with get() e.g. $val = $ref_node->get('field_status')->value;
You can also loop thru the referenced entities with:
foreach ($node_array as $node) {
$nid = $node->id();
}Entity reference nodes and their fields
You can look at the referenced node's fields but you have to be aware of how you set the display mode.
foreach ($node->field_my_entity_reference as $reference) {
// if you chose "Entity ID" as the display mode for the entity reference field,
// the target_id is the ONLY value you will have access to
echo $reference->target_id; // 1 (a node's nid)
// if you chose "Rendered Entity" as the display mode, you'll be able to
// access the rest of the node's data.
echo $reference->entity->title->value; // "Moby Dick"
}Often, you've just loaded the node with Node::load() so you have a node object and refer to reference fields like:
$vendor_url = $node->field_sf_contract_ref->entity->field_vendor_url->value;Load the taxonomy terms from a term reference field
The referencedEntities returns an array of term objects, so no need to load() them separately.
if ($node) {
$topics = $node->get('field_ref_tax')->referencedEntities();
foreach ($topics as $topic) {
$term_name = $topic->getName();
}
}Retrieve a URL field
External links
You can get the URL (for external links) and then just the text part. Note this doesn't work for internal links. Note also that this slightly convoluted example has a reference field field_sf_contract_ref which has a link to another entity and the field_vendor_url->first()->getUrl() is the important part. Also, note, this is a single-value field (not a multivalue field -- so the first() call is a little disturbing)
$vendor_url = $node->field_sf_contract_ref->entity->field_vendor_url->first()->getUrl();
if ($vendor_url) {
$vendor_url = $vendor_url->getUri();
//OR
$vendor_url = $vendor_url->toString();
}A slightly simpler example from modules/custom/tea_teks/modules/tea_teks_srp/src/Form/SrpAddEditCitationForm.php
$citation_link = $citation->get('field_link');
if (!$citation_link->isEmpty()) {
$citation_link = $citation->field_link->first()->getUrl()->toString();
}Internal links
For internal links, use getUrl() for the URL and ->title for the title.
$instructions_node = Node::load($order_type_instructions_nid);
if ($instructions_node) {
$order_link = $instructions_node->field_link->first();
if ($order_link) {
$uri = $order_link->uri;
$variables['order_link_title'] = $order_link->title;
$order_url = $order_link->getUrl();
if ($order_url) {
$variables['order_type_link'] = $order_url;
}
}
}How to get Node URL alias or Taxonomy Alias by Node id or Term ID
Drupal uses Url objects to easily generate and manipulate paths. The easiest way is to load the entity and convert it to a URL object:
$node = Node::load(1234)
$url_object = $node->toUrl();This can now be converted to a string
$href = $url_object->toString();If an absolute URL is needed, that's easy too:
$href = $url_object->setAbsolute()->toString();This will return a path in the form node/123
$current_path = \Drupal::service('path.current')->getPath();How to set a URL Alias
Since Drupal 9, url aliases are entities, so:
From: /Users/selwyn/Sites/dir/web/modules/custom/dir/dir.module
$node_path = "/node/$nid";
$new_url = $parent_url_alias . $url_alias;
/** @var \Drupal\path_alias\PathAliasInterface $path_alias */
$path_alias = \Drupal::entityTypeManager()->getStorage('path_alias')->create([
'path' => $node_path,
'alias' => $new_url,
'langcode' => 'en',
]);
$path_alias->save();Get a node's menu item and more
Here we get the current route's menu item using its nid, reset the link off the array, and we can extract the URL and other exciting things. Mostly, you want to check its children, parents, etc. Here we grab its URL.
/** @var \Drupal\Core\Menu\MenuLinkManagerInterface $menu_link_manager */
$menu_link_manager = \Drupal::service('plugin.manager.menu.link');
$links = $menu_link_manager->loadLinksByRoute('entity.node.canonical', ['node' => $nid]);
$link = reset($links);
$urlobject = $link->getUrlObject();
$url_string = $urlobject->toString();
$x = $link->getParent(); //get the parent menu item GUID.
$y = $link->getTitle(); // get the title of the menu item.
$menu_name = $link->getMenuName(); // get the menu name e.g. "main"Find a node using its uuid
/**
* Tries to get node for given uuid if it exists.
*
* @param string $uuid
* UUID to search for existing node.
*
* @return \Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityInterface[]|null
* Node object or NULL.
*
* @throws \Drupal\Component\Plugin\Exception\InvalidPluginDefinitionException
* @throws \Drupal\Component\Plugin\Exception\PluginNotFoundException
*/
public function getExistingUpdateNode(string $uuid) {
try {
$existing_node = \Drupal::entityTypeManager()
->getStorage('node')
->loadByProperties(['uuid' => $uuid]);
return $existing_node;
} catch (RequestException $e) {
watchdog_exception('ncs_infoconnect', $e);
return NULL;
}
}Retrieve Node ID(NID) or Taxonomy term ID from a Drupal alias or path
If alias-path does not exist, it will return the same argumented string.
The first example will work for the node, the second for the taxonomy, and the third for the users. For Drupal 8.8.0 and later, use path_alias.manager
//Node
$path = \Drupal::service('path.alias_manager')->getPathByAlias('/alias-path');
if (preg_match('/node\/(\d+)/', $path, $matches))
$nodeID = $matches[1];
//Taxonomy term
$path = \Drupal::service('path.alias_manager')->getPathByAlias('/alias-path');
if (preg_match('/taxonomy\/term\/(\d+)/', $path, $matches))
{
$termID = $matches[1];
}
//User
$path = \Drupal::service('path.alias_manager')->getPathByAlias('/alias-path');
if (preg_match('/user\/(\d+)/', $path, $matches))
{
$userID = $matches[1];
}Retrieve all nodes with a matching taxonomy term
$nodes = \Drupal::entityTypeManager()->getStorage('node')->loadByProperties([
'field_tags' => $term_id,
]);
## Load first 5 nodes that have a matching taxonomy term
```php
protected function loadFirstOpinion($term_id) {
$storage = \Drupal::entityTypeManager()->getStorage('node');
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->condition('status', 1)
->condition('type', 'opinion')
->condition('field_category', $term_id, '=')
->range(0, 5);
$nids = $query->execute();
$nodes = $storage->loadMultiple($nids);
$ra = [];
foreach ($nodes as $node) {
$ra[] = [
'#type' => 'markup',
'#markup' => '<p>' . $node->getTitle(),
];
}
return $ra;How to uncache a particular page or node
This will cause Drupal to rebuild the page internally, but won't stop browsers or CDNs from caching.
\Drupal::service('page_cache_kill_switch')->trigger();You can use this statement in node_preprocess, controller, etc.
You will need a custom module to implement setting max-age to 0, like this. In a .module file:
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\Display\EntityViewDisplayInterface;
function drt_node_view_alter(array &$build, EntityInterface $entity, EntityViewDisplayInterface $display) {
$bundle = $entity->bundle();
if ($bundle == 'search_home') {
$build['#cache']['max-age'] = 0;
\Drupal::service('page_cache_kill_switch')->trigger();
}Note, the above custom module is called drt. You would use your own module name instead of drt when naming the function.
Get boolean Field
Boolean fields show up as 0 or 1, so a simple test using if $val will return true for yes/on and false for no/off.
$val = $contract_node->field_erate_certification->value;
if ($val) {
$erate_certification = "Yes";
}Date Field
Date fields in Drupal are stored in UTC date strings. When you load them, you have some options. Probably grabbing the field->date is the best, so you can use all the goodness of the DrupalDateTime class. If you need to do calculations involving Unix timestamps, then ->getTimestamp is useful, although DrupalDateTime can do all kinds of calculations too.
$end_date = $contract_node->field_contract_end_date->value;
$end_date = $contract_node->field_contract_end_date->date->getTimestamp();
$end_date = $contract_node->field_contract_end_date->date;
$formatted_date = $end_date->format('m/d/y');
field_contract_end_date ->value; //returns whatever the string is e.g. 2024-08-31
field_contract_end_date->date->getTimestamp(); // returns unix timestamp e.g. 1725105600
field_contract_end_date->date; // returns a DrupalDateTime object with all its goodness
$formatted_date = $end_date->format('m/d/y'); //Format the date nicely for outputA date field has two properties:
value to store the date in UTC and
date, a computed field returning a DrupalDateTime object, on which you can use the methods getTimestamp() or format():
// get unix timestamp
$timestamp = $node->field_date->date->getTimestamp();
// get a formatted date
$date_formatted = $node->field_date->date->format('Y-m-d H:i:s');Date Fields
See also Queries: “Query the creation date (among other things) using entityQuery”
These are stored in the Drupal database as varchar 20 strings.
$d = date("m/d/Y",$timestamp);printing this date will return: 08/16/2018
From https://www.drupal.org/node/1834108
There is a DrupalDateTime object which is used like this:
$date = DrupalDateTime::createFromDateTime($datetime);
$date = DrupalDateTime::createFromArray($array);
$date = DrupalDateTime::createFromTimestamp($timestamp);
$date = DrupalDateTime::createFromFormat($format, $time);e.g. to create a DrupalDateTime
$format = 'Y-m-d H:i';
$start_date = DrupalDateTime::createFromFormat($format, “2019-01-01 00:00");In the database, the created and changed fields use a Unix timestamp. e.g look in node_field_revision
This is an int 11 field in the db with a value like 1525302749 (Note, negative values are dates before 1970 or epoch which require some slightly special magic)
If you add a Date field to a content type, its data looks like 2019-05-15T21:32:00 (varchar 20)
See the next item below for how to query the created and changed fields and also the fun you have to go through to query date fields.
When writing Drupal dates to the database, you need to go thru some machinations. Here are some details to explain the timezone.
$date_string = "2020-08-24T15:28:04+00:00";
$tz = \Drupal::currentUser()->getTimezone();
// specify timezone as "America/Chicago"
$given = new \Drupal\Core\Datetime\DrupalDateTime($date_string, $tz);
// specify timezone as "UTC"
$given = new \Drupal\Core\Datetime\DrupalDateTime($date_string, "UTC");
// specify UTC as the timezone
$given->setTimezone(new \DateTimeZone("UTC"));
// The date string appears adjusted to UTC
$newstring = $given->format("Y-m-d\Th:i:s");Date Range Field doesn't display correct timezone
If you use a date range field in your content type and try to display the time part in a template, Drupal will cleverly display the UTC version (not your current timezone version) so the time will be off by potentially ~6 hours.
Using the field field_event_date, here is the twig template code to display the date. You'd expect it to show the correct timezone
{{ node.field_event_date.0.value|date('g:ia') }} - {{ node.field_event_date.0.end_value|date('g:ia') }}If you simply used {{ content }} all fields are displayed correctly -- timezone is correct.
If you use {{ content.field_date_start }} - timezone show correctly also
But I want to grab the time only to display separately from the date and put this in the twig template:
{{ node.field_date_start.value|date("g:ia") }}It fails.
From
The solution is to create a variable in the template_preprocess_node. Append 'UTC' to the datetime string and make a timestamp so you get the UTC time (which matches what is in the Drupal DB). Grab the user's timezone for conversion purposes. Use the Drupal date.formatter service to format a timestamp (using the timezone) and you are good to go.
function txglobal_preprocess_node(&$variables) {
..
if ( ($node_type == 'event') ) {
$node = $variables['node'];
$timezone = drupal_get_user_timezone();
$formatter = \Drupal::service('date.formatter');
$dates = $node->get('field_event_date')->getValue();
$date_start = $dates[0]['value'];
$time = strtotime($date_start.' UTC');
$start_time = $formatter->format($time, 'custom', 'g:ia', $timezone);
// $start_time = date("g:ia", $time);
$date_end = $dates[0]['end_value'];
$time = strtotime($date_end.' UTC');
$end_time = $formatter->format($time, 'custom', 'g:ia', $timezone);
// $date_start = new DateTime($date_start);
// $timestamp_start = $date_start->getTimestamp();
// $start_time = $formatter->format($timestamp_start, 'custom', 'g:ia', $timezone);
// $end_time = $formatter->format($date_end, 'custom', 'g:ia', $timezone);
$variables['start_time'] = $start_time;
$variables['end_time'] = $end_time;
}and then in the template, use
{{ start_time }} - {{ end_time }}Interestingly, if you use the smart_date module, you might use this version. Notice that dates are already stored as timestamps, so you don't have to first convert them.
if ( $node_type == 'event' && $view_mode == 'default' ) {
$timezone = drupal_get_user_timezone();
$formatter = \Drupal::service('date.formatter');
$d = $node->get('field_smart_event_date')->getValue();
$d0s = $d[0]["value"]; //first date start time
$d0e = $d[0]["end_value"]; //first date end time
$start_time = $formatter->format($d0s, 'custom', 'g:ia');
$end_time = $formatter->format($d0e, 'custom', 'g:ia', $timezone);
$variables['start_time'] = $start_time;
$variables['end_time'] = $end_time;
}Date Range
// formatted start date
$start_date_formatted = $node->field_date->start_date->format('Y-m-d H:i:s');
// formatted end date
$end_date_formatted = $node->field_date->end_date->format('Y-m-d H:i:s');Date Range fields: Load start and end values
Start date and end date.
$node->get('field_cn_start_end_dates')->value
$node->get('field_cn_start_end_dates')->end_valueDate Fields: Load or save them
Because date fields in Drupal are stored in strings, when you use get() or set(), they are still strings.
$node->get('field_cn_start_end_dates')->value
$node->set('field_cn_end_date', $end_date);If you want to manipulate them, convert them to DrupalDateTime objects, then convert them back to strings
Creating a new DrupalDateTime object is done like this:
use Drupal\Core\Datetime\DrupalDateTime;
$date = DrupalDateTime::createFromFormat('j-M-Y', '20-Jul-2019');
$date = new DrupalDateTime('now'); // grab current dateTime using NON static
$date->format('l, F j, Y - H:i'); // format it
// prints out nicely formatted version: Tue, Jul 16, 2019 - 11:34:am
$date = new DrupalDateTime('now'); // grab current dateTime
// Or print $date->format('d-m-Y: H:i A');
// prints out: 16-07-2019: 11:43 AMHow about with timezones?
$date = new DrupalDateTime();
$date->setTimezone(new \DateTimeZone('America/Chicago'));
print $date->format('m/d/Y g:i a');
// The above prints current time for given Timezone
// prints : 07/16/2019 10:59 am
// Another variation of the above except it takes specific date and UTC zone
$date = new DrupalDateTime('2019-07-31 11:30:00', 'UTC');
$date->setTimezone(new \DateTimeZone('America/Chicago'));
print $date->format('m/d/Y g:i a');
// prints 07/31/2019 6:30 amThe code below shows adding $days (an integer) to the date value retrieved from the field: field_cn_start_date.
Don't forget to add the use statement.
use Drupal\Core\Datetime\DrupalDateTime;
$start_date_val = $node->get('field_cn_start_date')->value;
$days = intval($node->get('field_cn_suspension_length')->value) - 1;
//$end_date = DrupalDateTime::createFromFormat('Y-m-d H:i:s', $start_date_val . " 00:00:00");
$end_date = DrupalDateTime::createFromFormat('Y-m-d', $start_date_val );
$end_date->modify("+$days days");
$end_date = $end_date->format("Y-m-d");
$node->set('field_cn_end_date', $end_date);Comparing DrupalDateTime values
DrupalDateTimes are derived from DateTimePlus which are wrappers for PHP DateTime class. So you can use that functionality to do comparisons
date_default_timezone_set('Europe/London');
$d1 = new DateTime('2008-08-03 14:52:10');
$d2 = new DateTime('2008-01-03 11:11:10');
var_dump($d1 == $d2);
var_dump($d1 > $d2);
var_dump($d1 < $d2);outputs:
bool(false)
bool(true)
bool(false)Date with embedded timezone
Here you have a date string with an embedded timezone so you can make it into a DrupalDateTime and then format it into a usable string you can store in the db.
use Drupal\Core\Datetime\DrupalDateTime;
$date_string = "2020-08-24T15:28:04+00:00";
$given = new DrupalDateTime($date_string);
$newstring = $given->format("Y-m-d\Th:i:s");Has something expired?
Checking to see if the expiration_date has passed. The field_expiration_date is a standard Drupal date field in the sf_resellers content type.
$source_node = $node_storage->load($nid);
$expiration_date = $source_node->field_expiration_date->value;
// Use an expiration date to unpublish expired resellers to hide them.
$status = 1;
if ($expiration_date) {
$expirationDate = DrupalDateTime::createFromFormat('Y-m-d', $expiration_date);
$now = new DrupalDateTime();
if ($expiration_date < $now) {
$status = 0;
}
}TODO: date fields are stored in UTC. Need to factor in timezone.
Load or save Drupal Date fields
Date fields in Drupal are stored in strings
If you want to load them, just get(), as below and to save them, use set.
$node->get('field_cn_start_end_dates')->value
$node->set('field_cn_end_date', $end_date);If you want to manipulate them, convert them to DrupalDateTime objects, then convert them back to strings like this. $days here is an int and we are adding that to the date value. Don't forget to add the use statement.
use Drupal\Core\Datetime\DrupalDateTime;
$start_date_val = $node->get('field_cn_start_date')->value;
$days = intval($node->get('field_cn_suspension_length')->value) - 1;
// $end_date = DrupalDateTime::createFromFormat('Y-m-d H:i:s', $start_date_val . " 00:00:00");
$end_date = DrupalDateTime::createFromFormat('Y-m-d', $start_date_val );
$end_date->modify("+$days days");
$end_date = $end_date->format("Y-m-d");
$node->set('field_cn_end_date', $end_date);Here you have a slightly funny date string, you make it into a DrupalDateTime and then format it into a usable string you can store in the database.
use Drupal\Core\Datetime\DrupalDateTime;
$date_string = "2020-08-24T15:28:04+00:00";
$given = new \Drupal\Core\Datetime\DrupalDateTime($date_string);
$newstring = $given->format("Y-m-d\Th:i:s");Retrieve node creation date and format it
Here I query the database for a node and return a string version of the date. It probably makes more sense to return the date and do the formatting at the theme level. Note, this will handle epoch dates before 1970.
use Drupal\Core\Datetime\DrupalDateTime;
protected function loadFirstOpinionYear($term_id) {
$storage = \Drupal::entityTypeManager()->getStorage('node');
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->condition('status', 1)
->condition('type', 'opinion')
->condition('field_category', $term_id, '=')
->sort('title', 'ASC') //DESC
->range(0, 1);
$nids = $query->execute();
if ($nids) {
$node = $storage->load(reset($nids));
}
$time = $node->get('created')->value;
$d = new DrupalDateTime("@$time"); //can use either this
$d = new \DateTime("@$time"); // or this..
$str = $d->format('Y-m-d H:i:s');
return $str;
}Retrieve node creation or changed date and format it
Both created and changed are stored as Unix epoch timestamps the node_field_data table. Here I query the database for a node and return a string version of the date. Note, this will handle epoch dates before 1970.
use Drupal\Core\Datetime\DrupalDateTime;
protected function loadFirstOpinionYear($term_id) {
$storage = \Drupal::entityTypeManager()->getStorage('node');
$query = \Drupal::entityQuery('node')
->condition('status', 1)
->condition('type', 'opinion')
->condition('field_category', $term_id, '=')
->sort('title', 'ASC') //DESC
->range(0, 1);
$nids = $query->execute();
if ($nids) {
$node = $storage->load(reset($nids));
}
$time = $node->get('created')->value;
$d = new DrupalDateTime("@$time"); //can use either this
$d = new \DateTime("@$time"); // or this..
$str = $d->format('Y-m-d H:i:s');
return $str;
}Date Field and Date with no time (remove time)
Use the setTime() function to remove the time part of a datetime so we can make comparisons of just the date.
function ogg_mods_cn_form_validate($form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
$start_date = $form_state->getValue('field_cn_start_date');
if ($start_date) {
$start_date = $start_date[0]['value'];
$start_date->setTime(0, 0, 0);
$now = new Drupal\Core\Datetime\DrupalDateTime();
$now->modify("-2 days");
$now->setTime(0, 0, 0);
\Drupal::messenger()->addMessage("Start date = $start_date");
\Drupal::messenger()->addMessage("Now date - 2 days = $now");
if ($start_date < $now) {
$form_state->setErrorByName('edit-field-cn-start-date-0-value-date', t('The starting date is more than 2 days in the past. Please select a later date'));
}
}
}Smart date (smart_date) load and format
Load the smart date field and use the drupal date formatting service. Smart date fields are always stored as Unix timestamp values e.g. 1608566400 which need conversion for human consumption.
$start = $node->field_when->value;
$formatter = \Drupal::service('date.formatter');
$start_time = $formatter->format($start, 'custom', 'm/d/Y g:ia'); //12/21/2020 10:00 amAlternatively, you could load it, create a DrupalDateTime and then format it
$start = $node->field_when->value;
$dt = DrupalDateTime::createFromTimestamp($start);
$start_date = $dt->format('m/d/y'); //returns 12/21/20
$start_time = $dt->format('g:ia'); // returns 10:00amSmart date (smart_date) all-day
To check if a smart date is set to all day, check the duration. If it is 1439, that means all day.
$start_ts = $node->field_when->value;
$start_dt = DrupalDateTime::createFromTimestamp($start_ts);
$start_date = $start_dt->format('m/d/Y');
$duration = $node->field_when->duration; //1439 = all day
if ($duration == 1439) {
$start_time = "all day";
}
else {
$start_time = $start_dt->format('g:ia');
}Smart date (smart_date) range of values
//Event start date.
$whens = $node->get('field_when'); //produces SmartDateFieldItemList
// Each $when is a \Drupal\smart_date\Plugin\Field\FieldType\SmartDateItem
foreach ($whens as $when) {
$start = $when->value;
$end = $when->end_value;
$duration = $when->duration; //1439 = all day
$tz = $when->timezone; //"" means default. Uses America/Chicago type format.
}You can also peek into the repeating rule and repeating rule index. These are in the smart_date_rule table and I believe the index identifies which item is in the instances column.
$rrule = $when->rrule;
$rrule_index = $when->rrule_index;hook_node_presave or hook_entity_type_presave
When you want to fiddle with a node as it is being saved, use hook_node_presave()
Note, there is some good date arithmetic here
/**
* Implements hook_ENTITY_TYPE_presave().
*/
function ogg_mods_node_presave(NodeInterface $node) {
switch ($node->getType()) {
case 'catastrophe_notice':
$end_date = NULL != $node->get('field_cn_start_end_dates')->end_value ? $node->get('field_cn_start_end_dates')->end_value : 'n/a';
$govt_body = NULL != $node->field_cn_governmental_body->value ? $node->field_cn_governmental_body->value : 'Unnamed Government Body';
$start_date_val = $node->get('field_cn_start_date')->value;
$accountProxy = \Drupal::currentUser();
$account = $accountProxy->getAccount();
// Anonymous users automatically fill out the end_date.
if (!$account->hasPermission('administer catastrophe notice')) {
$days = intval($node->get('field_cn_suspension_length')->value) - 1;
$end_date = DrupalDateTime::createFromFormat('Y-m-d', $start_date_val);
$end_date->modify("+$days days");
$end_date = $end_date->format("Y-m-d");
$node->set('field_cn_end_date', $end_date);
}
// Always reset the title.
$title = substr($govt_body, 0, 200) . " - $start_date_val";
$node->setTitle($title);
/*
* Fill in Initial start and end dates if this is an extension of
* a previously submitted notice.
*/
$extension = $node->get('field_cn_extension')->value;
if ($extension) {
$previous_notice_nid = $node->get('field_cn_original_notice')->target_id;
$previous_notice = Node::load($previous_notice_nid);
if ($previous_notice) {
$initial_start = $previous_notice->get('field_cn_start_date')->value;
$initial_end = $previous_notice->get('field_cn_end_date')->value;
$node->set('field_cn_initial_start_date', $initial_start);
$node->set('field_cn_initial_end_date', $initial_end);
}
}
break;
}
}Disable caching for a content type
If someone tries to view a node of content type search_home (entity of bundle search_home) caching is disabled and Drupal and the browser will always re-render the page. This is necessary for a page that is retrieving data from a third-party source, and you almost always expect it to be different. It wouldn't work for a search page to show results from a previous search.
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\Display\EntityViewDisplayInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Entity\Display\EntityViewDisplayInterface;
/**
* Implements hook_ENTITY_TYPE_view_alter().
*/
function dir_node_view_alter(array &$build, EntityInterface $entity, EntityViewDisplayInterface $display) {
$bundle = $entity->bundle();
if ($bundle == 'search_home') {
$build['#cache']['max-age'] = 0;
\Drupal::service('page_cache_kill_switch')->trigger();
}
}In the API docs ( https://api.drupal.org/api/drupal/core!lib!Drupal!Core!Entity!entity.api.php/function/hook_ENTITY_TYPE_view_alter/9.2.x ). They have an example where they check the view mode and dynamically add a field to the node. There is also a post_render callback function added to do some more magic. To implement, you'd have to replace ENTITY_TYPE with your entity type, such as node. See below:
function hook_ENTITY_TYPE_view_alter(array &$build, Drupal\Core\Entity\EntityInterface $entity, \Drupal\Core\Entity\Display\EntityViewDisplayInterface $display) {
if ($build['#view_mode'] == 'full' && isset($build['an_additional_field'])) {
// Change its weight.
$build['an_additional_field']['#weight'] = -10;
// Add a #post_render callback to act on the rendered HTML of the entity.
$build['#post_render'][] = 'my_module_node_post_render';
}
}Writing some JSON data into a long text field
It is sometimes useful to store JSON data into a long text field. I've used it for storing formatted status information about a complex process.
$aggregate_values = [
'citation_status' => $citation_status,
'accepted_votes' => $accepted_votes,
'rejected_votes' => $rejected_votes,
];
$aggregate_data = Json::encode($aggregate_values);
$citation_node->field_srp_agg_data_json[$vote_number] = $aggregate_data;
$citation_node->save();The JSON data is written into a multivalue long text field using the $vote_number index. So if $vote_number is 0, this will be the first value. If it is 1, then this will be written into the second value. This is what it looks like in Drupal on a node edit screen.
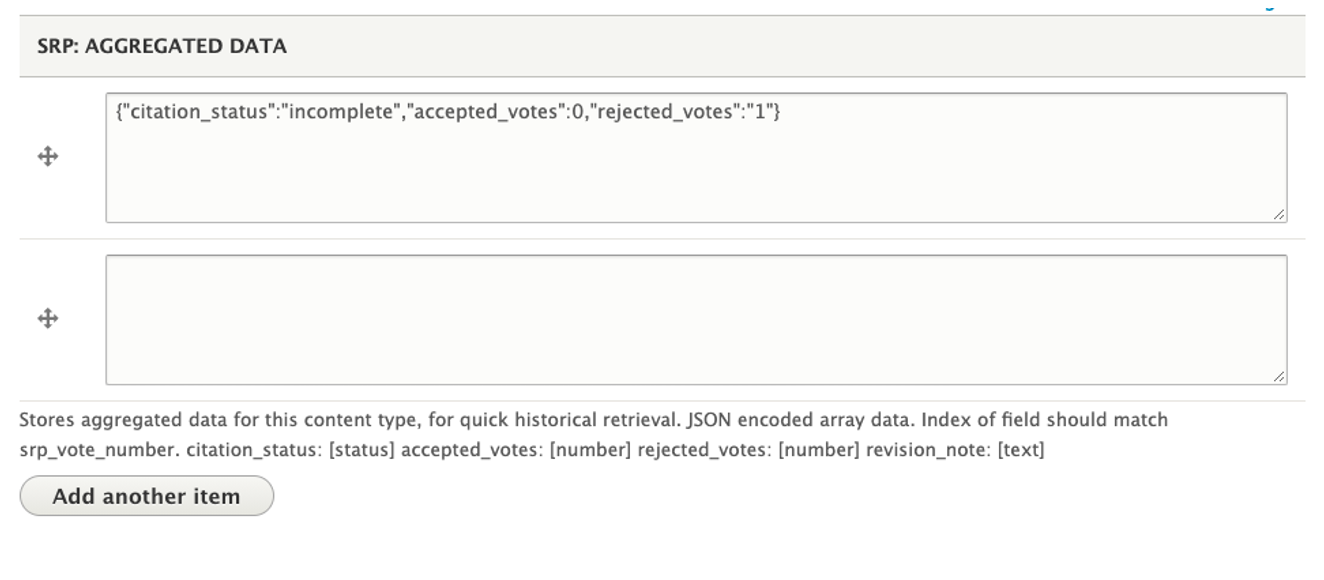
Create a node with an image
use \Drupal\node\Entity\Node;
use \Drupal\file\Entity\File;
// Create file object from remote URL.
$data = file_get_contents('https://www.drupal.org/files/druplicon.small_.png');
$file = file_save_data($data, 'public://druplicon.png', FILE_EXISTS_REPLACE);
// Create node object with attached file.
$node = Node::create([
'type' => 'article',
'title' => 'Druplicon test',
'field_image' => [
'target_id' => $file->id(),
'alt' => 'Hello world',
'title' => 'Goodbye world'
],
]);
$node->save();Puzzles
What can I do with a call to first() on an entity reference field?
After loading a node, I want to see the value in an entity reference field. I can call referencedEntities to pull out its values and loop thru them -- I get Nodes in that instance.
$refs = $node_to_update->get('field_sf_account_ref')->referencedEntities();
if ($refs) {
$ref = reset($refs);
$node_to_update_sf_account_nid = $ref->id();However, if I call ->first(), I get an EntityReferenceItem. I'm curious how I could use this -- would I want to?
$refs = $node->get('field_sf_dir_contact_ref')->first(); //returns an EntityReferenceItem.